
- #QUOTIENT RULE CALCULUS LOW HOW TO#
- #QUOTIENT RULE CALCULUS LOW PLUS#
- #QUOTIENT RULE CALCULUS LOW FREE#
You can clean it up if you wish, but most teachers will be okay if you leave it here, you may also factor a bit if you would like. Now this lovely function is your second derivative. It is provable in many ways by using other derivative rules. Basically its the (derivative of first function ) second function - (derivative of second function) first function divided by second function squared. 1 2 3 Let where both f and g are differentiable and The quotient rule states that the derivative of h(x) is. #((16x^2+8x+1)(24x^2+6x)-(8x^3+3x^2+1)(32x+8))/(16x^2+8x+1)^2# In calculus, the quotient rule is a method of finding the derivative of a function that is the ratio of two differentiable functions. Now we must find the derivative of this, having fun yet? The derivative rules (addition rule, product rule) give us the overall wiggle. Which simplifies to ( Going to go ahead and put the derivatives here): Now, we can make a bigger machine from smaller ones (h f + g, h f g, etc.). By using normal differentiating rules, we know that f (x)2x and g (x)12x 2.
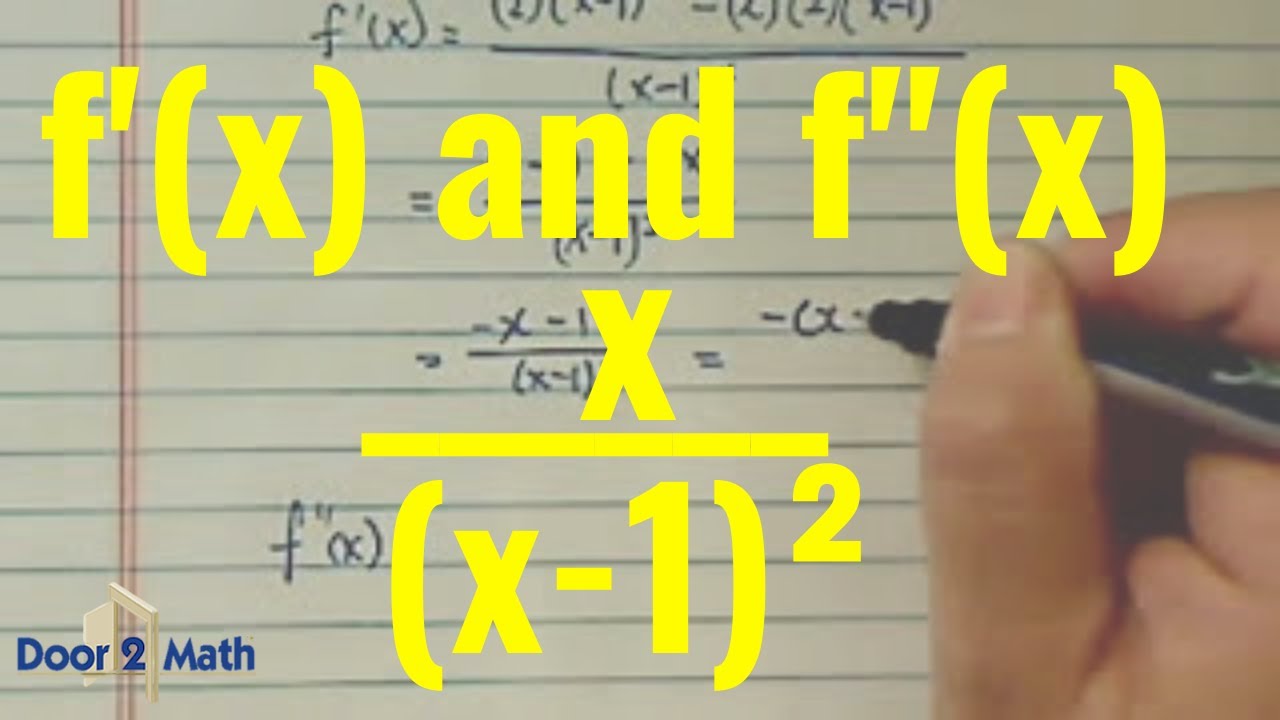
Our functions f and g are f (x)x 2 and g (x)4x 3 -7. Now in order to find the second derivative, you must take the derivative of the first derivative, but I'm going to clean it up first. Now this expression above is your first derivative. But let me just state the quotient rule right now. Now that we have that, we plug in each value into the quotient rule. The quotient rule, I'm gonna state it right now, it could be useful to know it, but in case you ever forget it, you can derive it pretty quickly from the product rule, and if you know it, the chain rule combined, you can get the quotient rule pretty quick.
#QUOTIENT RULE CALCULUS LOW FREE#
Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus. We find the derivatives of the numerator and denominator using the power rule. Rewrite the expression using the negative exponent rule bn 1 bn b - n 1. We take the denominator times the derivative of the numerator (low d-high). #(x^3+x)/(4x+1)# derivatives: #(3x^2+1)/4# What is the Quotient rule Basically, you take the derivative of f multiplied by g, subtract f multiplied by the derivative of g, and divide all that by g (. In calculus, the quotient rule is a method of finding the derivative of a function that is. So, if we write down the function next to it's derivatives, it would look like this: It returns the largest profit of buying low and selling high. We will also recognize that the memory trick for the Quotient Rule is a simple variation of the one we used.
#QUOTIENT RULE CALCULUS LOW HOW TO#
In this section, we will learn how to apply the Quotient Rule, with additional applications of the Chain Rule. So the denominator times the derivative of the numerator minus the numerator times the derivative of the denominator divided by the denominator squared. To find the derivative of a function resulted from the quotient of two distinct functions, we need to use the Quotient Rule.

Then you divide all that by the bottom function squared.Ī trick to remembering this is "low d-high minus high d-low, over the square of low we go.The quotient rule goes as follows: #dy/dx f(x)/g(x) = (g(x)f'(x)-f(x)g'(x))/g(x)^2#Īn easy way to remember this is the mnemonic "low d hi - hi d low over low squared." D meaning derivative. The quotient rule is used when you have to find the derivative of a function that is the quotient of two other functions for which derivatives exist.įor the quotient rule, you take the bottom function in a fraction mulitplied by the derivative of the top function and then subtract the top function multiplied by the derivative of the bottom function. Let f (x) e x and g (x) 3x 3, then apply the quotient rule: 2.
#QUOTIENT RULE CALCULUS LOW PLUS#
You take the left function multiplied by the derivative of the right function and add it with the right function multiplied by the derivative of the left function.Ī trick to remembering this is "left d-right plus right d-left." The product rule is used when you have two or more functions, and you need to take the derivative of them. log(4x+1) Now theres a rule in logarithms which is: log(ab) blog(a). Three of these rules are the product rule, the quotient rule, and the chain rule. Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus.

There are different rules for finding the derivatives of functions. The quotient rule is the formula for taking the derivative of the quotient of two functions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
